- Home
- »
- LED Academy
- »
- LED Display Technology Basics
LED display technology basics
Table of Contents
LED Technology Development History
LED is the abbreviation of Light Emitting Diode, and its Chinese name is light-emitting diode. Its unique optoelectronic properties make it widely used in many fields and equipment, such as various electrical remote controls, equipment indicator lights, LED lighting and displays, etc.
In 1907, scientists at the Marconi Laboratory in the UK first deduced that semiconductor PN junctions can emit light under certain conditions, laying the physical foundation for the invention of LED.
In 1927, Russian scientists independently produced the world’s first LED, and their research results were published in scientific magazines in Russia, Germany and the UK. However, for a period of time afterwards, people did not realize its huge potential and application value, and LED only remained at the technical level.
In 1955, physicists at the Radio Corporation of America first discovered the infrared radiation effect of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and other semiconductor alloys, and physically realized the light emission of diodes. Because it emits infrared rays instead of visible light, this research is of great significance to the development of LED.
In 1961, scientists at Texas Instruments (TI) discovered that gallium arsenide would release infrared radiation when an electron flow was applied. They were the first to produce infrared LEDs for commercial use and obtained a patent for the invention of gallium arsenide infrared LEDs. After official commercial use, infrared LEDs were widely used in various sensors and optoelectronic devices, such as remote controls for various household appliances.
In 1962, researchers at General Electric (GE) invented an LED that could emit red visible light and was called the “father of light-emitting diodes.” At that time, LEDs had to be made by hand and each sold for as much as $10. In 1963, the researcher left General Electric and became a professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering at the University of Illinois, further advancing LED research.
In 1972, the researcher’s students invented the first orange-yellow LED, which was 10 times brighter than the previous red visible light LED, marking an important first step for LEDs to improve luminous efficiency.
In the late 1970s, people had developed LEDs that produced red, orange, yellow, green, and emerald green light, but there were no blue or white LEDs. Although full-color LED display was not possible at the time, the luminous efficiency of LEDs was greatly improved. In the mid-1970s, when LEDs produced green, yellow, and orange light, the luminous efficiency was 1 lumen/watt; by the mid-1980s, the use of gallium arsenide and aluminum phosphide led to the birth of the first generation of high-brightness red, yellow, and green LEDs, with a luminous efficiency of 10 lumens/watt.
In 1993, while working at Nichia Chemical Corporation in Japan, Shuji Nakamura invented blue LEDs using gallium nitride (GaN) and indium gallium nitride (InGaN). Before the emergence of blue LEDs, it was impossible to synthesize white light through the RGB system, and the LED light efficiency and brightness were not high, so it could not be used in the lighting field.
In 1995, he invented green LED using indium nitride; in 1998, he made white LED using red, green and blue LEDs. The successful development of green and white LEDs marked the official entry of LED into the lighting field and was the most critical milestone in the development of LED lighting. Shuji Nakamura was also known as the “father of blue, green and white LEDs”.
In 1996, Nichia Chemical Industries, Ltd. first applied for a patent for the invention of white LED in Japan. The blue light emitted by the chip and the yellow light emitted by the activated phosphor complement each other to form white light. The emergence of blue and white LEDs has broadened the application field of LEDs and provided a technical basis for full-color LED displays, LED lighting and other applications.
By the early 21st century, LEDs could emit light of various colors in the visible spectrum, and could also display infrared and ultraviolet rays, with a luminous efficiency of more than 100 lumens/watt.
Development of LED display screens
With the continuous updating and development of LED production technology, people have found that LED, as a point light source, can be used as lighting or display screens after using more LED lamp beads at the same time.
In the 1970s, the early invention of GaP, GaAsP and other red and yellow LEDs began to be used for instrument indicators, displaying simple numbers and text, etc., becoming the earliest prototype of the development of LED display screens. However, due to the limitations of production processes and costs, LED display technology has not been vigorously developed.
In the early 1990s, LED semiconductor materials and production technologies became increasingly mature. After the invention of blue light LED by Nichia Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. of Japan, LED display screens had full-color display capabilities, and then LED display products gradually appeared and entered the consumer market. Limited by the control technology of LED display screens, LED display screens at that time were mainly used to display text and pictures, with low display brightness and grayscale levels, but the easy scalability of LED display screens made customers in the traditional LCD market realize its huge development potential.
In 1996, the former Ministry of Electronics commissioned LanTong Company to formulate the “General Specifications for LED Display Screens”. LED display screens truly became an independent industry, and the emergence of industry norms and standards accelerated the development of the
In 1998, the China Optics and Optoelectronics Industry Association established the LED Display Professional Committee; in January 2003, the China Optics and Optoelectronics Industry Association Light Emitting Diode Display Branch was formally established; in November 2006, it was changed to the China Optics and Optoelectronics Industry Association Light Emitting Diode Display Application Branch, marking the LED industry into standardized development.
Due to the limitations of LED lamp bead technology, early LED display screens were mainly monochrome and dual-color screens, such as red and red-green dual-color screens, which mainly displayed text and pictures.

Around 2000, full-color LED display screens based on three primary colors were officially put into commercial use. Due to their high display brightness and rich colors, they replaced the billboards used by traditional media and were installed in city main roads, intersections and commercial office buildings. Due to their excellent display effects and visual impact, full-color LED display screens ushered in a period of rapid development.
Applications of LED Displays
As a new type of display carrier, LED display screens are applied to more and more scenarios with their unique advantages. The mainstream application scenarios are as follows:
Airports, railway stations, bus stations, etc.: These places have large personnel mobility and large population, and are important places for media operators to promote advertising. As one of the best carriers for displaying advertisements and disseminating information, LED display screens have become standard equipment in modern airports and stations.

Stages, event sites, etc.: Various indoor/outdoor performing arts activities, TV live broadcasts, variety shows, etc., in order to present better stage effects, LED display screens will be used as an important part of the stage effects. The gorgeous display effects and video special effects directly affect the effect of the entire stage.
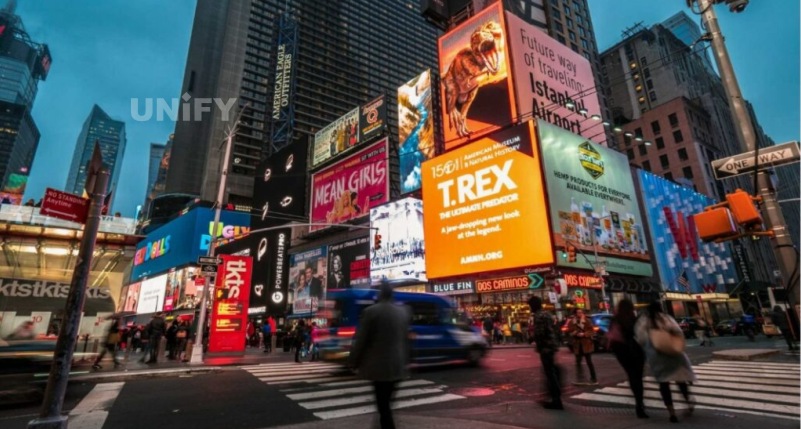

Hotels, conference rooms, school classrooms, etc.: In order to more vividly display promotional videos, work reports, teaching courseware, etc., these indoor places are equipped with LED display screens to replace traditional display media such as projectors, LED LCD screens, etc.
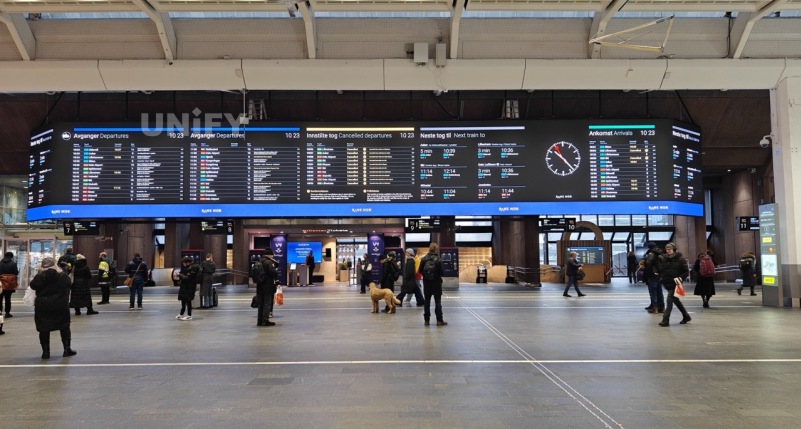

Traffic command and dispatch center, military, power dispatch room, urban integrated management platform, etc.: These occasions need to display a variety of different data, and uniformly dispatch and manage them, so they need to use large screens for display. LED display screens have become standard facilities in these occasions.

Urban traffic guidance, highway signs, etc.: With the continuous development of population and economy, the road traffic situation in my country’s large cities has become more severe. In order to display and guide vehicles in real time, more and more cities have installed LED screens on the roads.

Busy intersections, commercial complexes, office buildings and park squares in the city: Due to their superior geographical location, these locations are important occasions for advertising. The installation of LED displays activates the vitality of the installation site and becomes a landscape of the city.
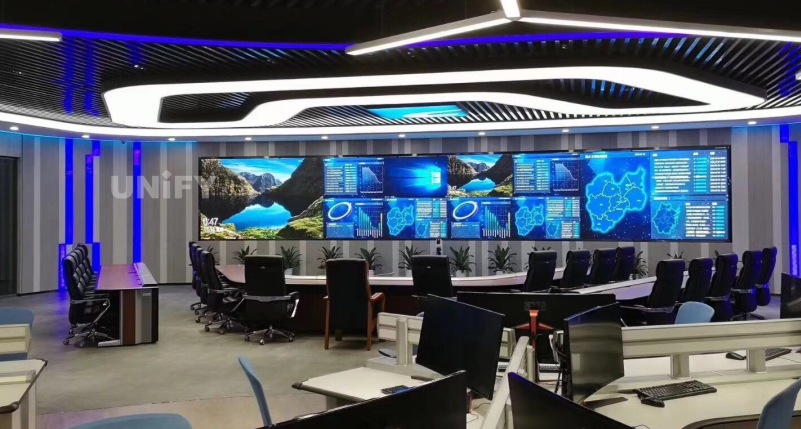

Characteristics of LED Display
Economic and technological development has driven the rapid development of cities. Especially since 2010, LED displays have been seen in more and more places, such as office buildings, large shopping malls , stations, conference rooms , squares, stages , and command centers. Its advantages and characteristics are mainly reflected in the following six aspects
High brightness
The brightness of traditional LCD screens and projectors is generally 500cd/m², while the brightness of screens using high-brightness LED lamp beads can reach 10,000cd/m². At such a high brightness, the LED screen can display clear images even under direct sunlight; even if used continuously for a long time, its annual brightness decay will not exceed 5%.High fidelity
The color grayscale of traditional display carriers is only 8bit, that is, a 256-level brightness variation range, while the LED screen equipped with a specific control system and driver chip can reach 16bit, that is, 65536 levels, which is 256 times that of traditional display devices. This allows the LED screen to present more color details, completely restore the original effect of the display material, and make the picture more vivid and gorgeous.
Unlimited expansion
Traditional LCD screens and projectors are limited by technology and size, making it difficult to expand arbitrarily. The LED screen is spliced by independent boxes, which can be infinitely expanded according to user needs, and can be spliced into irregular shapes to meet different display needs.
Economical
LED display screens are composed of light-emitting diode arrays. Light-emitting diodes have the characteristics of low power consumption. When in use, they only need a few milliamperes of current to work normally. Compared with LED and LCD displays of the same size, the power consumption of LED display screens is about half of that of LCD display screens, with significant economic benefits.
The operating temperature range of LED display screens is – 40 ~ 100 ℃, and the operating voltage range is 2.0 ~ 3.6V. The wide temperature range, low operating voltage, and unique structure of LED display screens make LED lamp beads have high reliability in various working environments such as outdoor and indoor. They can withstand the test of high temperature, severe cold, humidity, salt spray, dust, etc. all year round, and are very suitable for various commercial purposes.
Long life
LED has a PN junction inside. As long as a suitable forward voltage is applied to both ends of the PN junction, it will be lit, with very low power consumption and high luminous efficiency. Most of the energy is output in the form of light, so the heat generation is small. For the aging of electronic components, the amount of heat in the working environment will directly determine the working life and aging rate of the components. The extremely small heat generation of LED makes its working life reach 80,000 to 100,000 hours, greatly reducing the subsequent maintenance costs.
Recommend Products

Indoor LED Screen Case in USA: Elevate Your Church Services
Indoor LED Screen Case in USA: Elevate Your Church Services Home Table of Contents Introduction As churches across the USA seek to engage congregations with richer audio-visual experiences, the adoption of LED display technology has surged. Indoor LED screens are now a central feature in worship spaces, transforming the way messages and media are presented.

Synchronous Playback for LED Displays
Synchronized Playback for LED Displays Home Table of Contents Synchronized Playback for LED Displays After an LED display is configured, it needs to play content from a front-end input. When this content needs to be played in real-time, it is called synchronized playback for an LED display. Synchronized playback refers to the LED display playing
LED Display Basic Calculations
LED Display Basic Calculation Home Table of Contents Power Consumption Calculation In LED display related engineering projects, the power consumption of the screen power supply is a crucial parameter for evaluating screen performance and is closely tied to the safety of project construction. Incorrect calculation of the power consumption of an LED display in the early
